USD to INR: Best Time to Convert
The exchange rate between the United States Dollar (USD) and the Indian Rupee (INR) is a constantly fluctuating value that is influenced by a variety of factors, including interest rates, economic growth, political stability, inflation, market sentiment, and geopolitical events. As a result, determining the best time to convert USD to INR can be a challenging task. However, by analyzing historical exchange rate data and considering the current and future economic and political landscape, it is possible to identify the best times to convert USD to INR.
Historically, interest rates have played a significant role in determining the exchange rate between the USD and INR. If the interest rate in the United States is higher than the interest rate in India, there will be a higher demand for the USD, causing the exchange rate to increase. For example, in the early 2000s, the Federal Reserve increased interest rates in the United States, causing the value of the USD to increase relative to the INR. This trend continued until 2007, when the interest rate in India began to rise, causing the value of the INR to increase relative to the USD.
In addition to interest rates, economic growth has also had a significant impact on the exchange rate between the USD and INR. If the economy in the United States is growing rapidly, there will be a higher demand for the USD, causing the exchange rate to increase. Conversely, if the economy in India is growing rapidly, there will be a higher demand for the INR, causing the exchange rate to decrease. For example, in the late 1990s and early 2000s, the United States experienced a period of strong economic growth, causing the value of the USD to increase relative to the INR. Conversely, in the late 2000s and early 2010s, India experienced a period of rapid economic growth, causing the value of the INR to increase relative to the USD.
Political stability is another factor that can impact the exchange rate between the USD and INR. If there is political stability in the United States or India, there may be a higher demand for the currency of that country, causing the exchange rate to increase. Conversely, if there is political instability in either country, there may be a decrease in demand for the currency of that country, causing the exchange rate to decrease. For example, in the late 1990s and early 2000s, India experienced a period of political instability, causing the value of the INR to decrease relative to the USD. Conversely, in the late 2000s and early 2010s, India experienced a period of political stability, causing the value of the INR to increase relative to the USD.
Inflation is another factor that can impact the exchange rate between the USD and INR. If inflation is high in India, the value of the INR may decrease relative to the USD, causing the USD to INR exchange rate to rise. Conversely, if inflation is high in the United States, the value of the USD may decrease relative to the INR, causing the USD to INR exchange rate to fall. For example, in the late 1990s and early 2000s, India experienced high levels of inflation, causing the value of the INR to decrease relative to the USD.
Market sentiment and geopolitical events can also have a significant impact on the exchange rate between the USD and INR. For example, the global financial crisis of 2008 had a significant impact on the exchange rate between the USD and INR, causing the value of the USD to decrease relative to the INR. Similarly, the Brexit vote in 2016 and the trade tensions between the United States and China have also had an impact on the exchange rate between the USD and INR.
Looking ahead, India's rapid economic growth is likely to have a positive impact on the value of the Indian Rupee (INR) relative to the United States Dollar (USD). As the economy grows, there will be an increased demand for the INR, which will cause the value of the currency to increase. This, in turn, will result in a lower exchange rate between the USD and INR. India's rapid economic growth is driven by factors such as a growing middle class, increased investment, and favorable government policies. As more people become financially secure, they will have more disposable income to invest, which will help to drive the economy forward. Additionally, the government is taking steps to encourage investment, such as implementing policies to improve the business climate and encourage entrepreneurship. Furthermore, India's growing middle class is expected to drive consumer spending, which will increase demand for goods and services. This, in turn, will create jobs and drive economic growth, which will increase the demand for the INR. As the demand for the INR increases, the exchange rate between the USD and INR will decrease, making the INR more valuable relative to the USD.
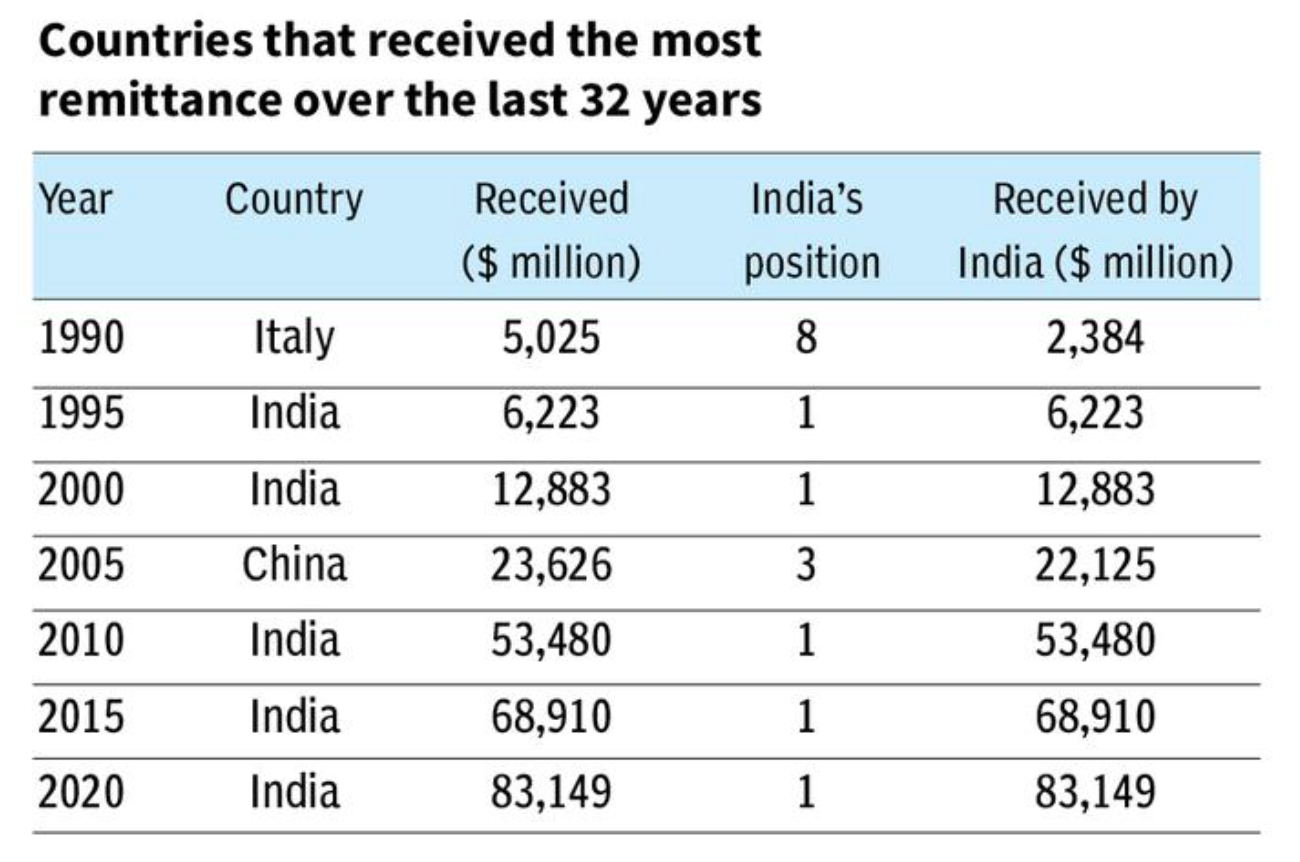
Reference:image:https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/data-stories/data-focus/india-topped-inward-remittance-list-for-23-of-27-years-since-1995/article66270971.ece
